Introduction
In the world of atomization technologies, the evolution of methods used to convert liquids into fine mist or vapor has seen significant advancements. Among these, two prominent technologies stand out: piezo and traditional atomization technologies. While both serve the same fundamental purpose, their operational principles, efficiency, and applications differ considerably.
Piezo atomization technology, particularly using piezo atomization chips, has become increasingly popular for applications requiring high precision, low energy consumption, and compact designs. On the other hand, traditional atomization methods, such as mechanical and ultrasonic atomization, rely on different physical principles and are widely used in various industrial applications.
What Is Atomization Technology?
Atomization refers to the process of breaking up a liquid into very fine droplets or particles. This process is crucial in various industries, including aerosol technology, fuel systems, agriculture (spray nozzles), and medical devices (inhalers). The technology can be categorized into several types based on how the atomization is achieved.
Key Atomization Methods:
- Piezo Atomization
- Traditional Atomization (Mechanical, Ultrasonic, etc.)
Piezo Atomization Technology
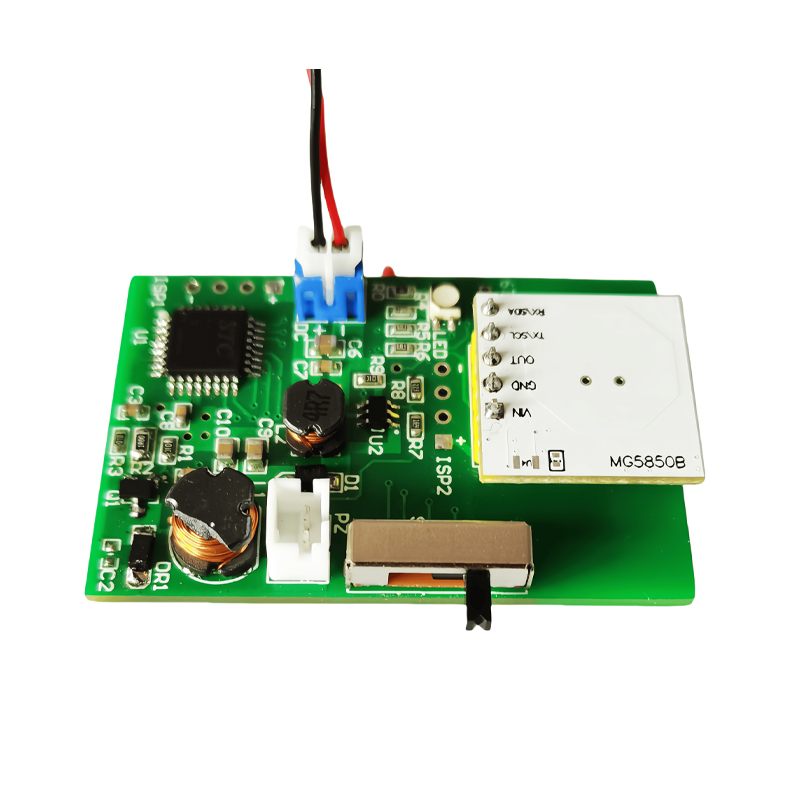
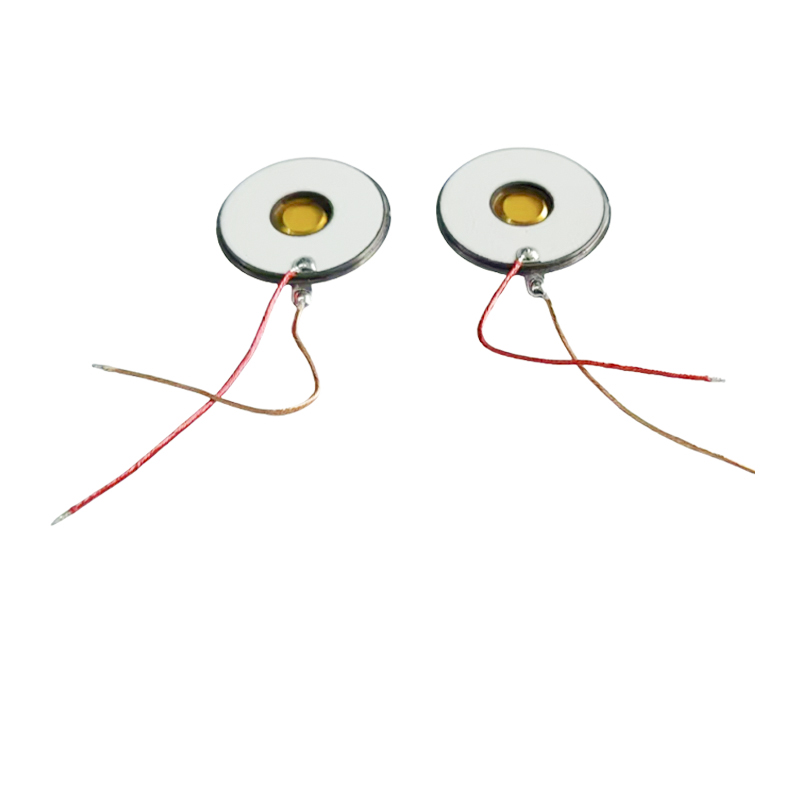
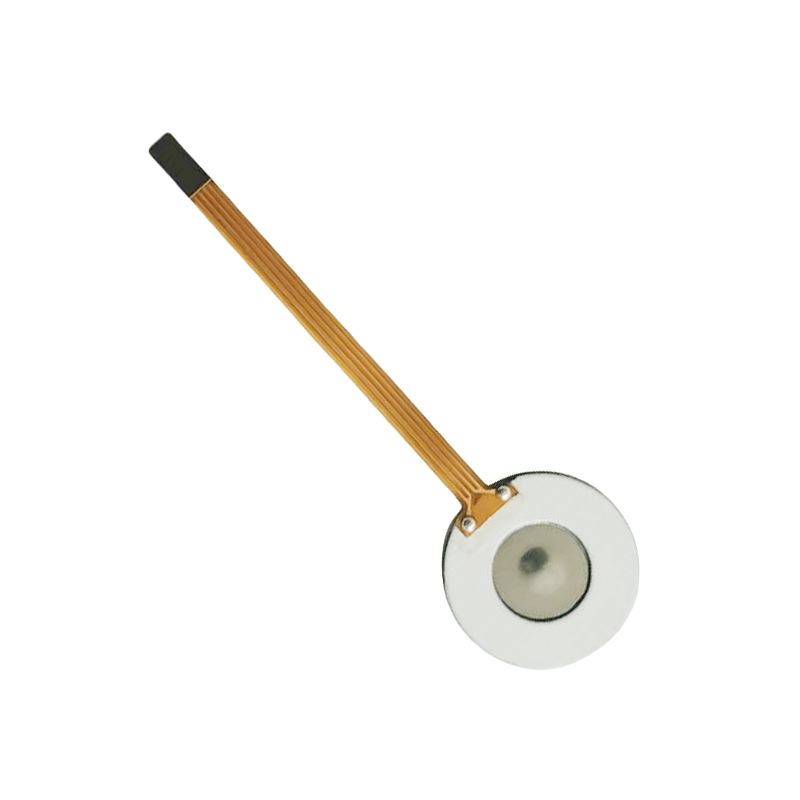
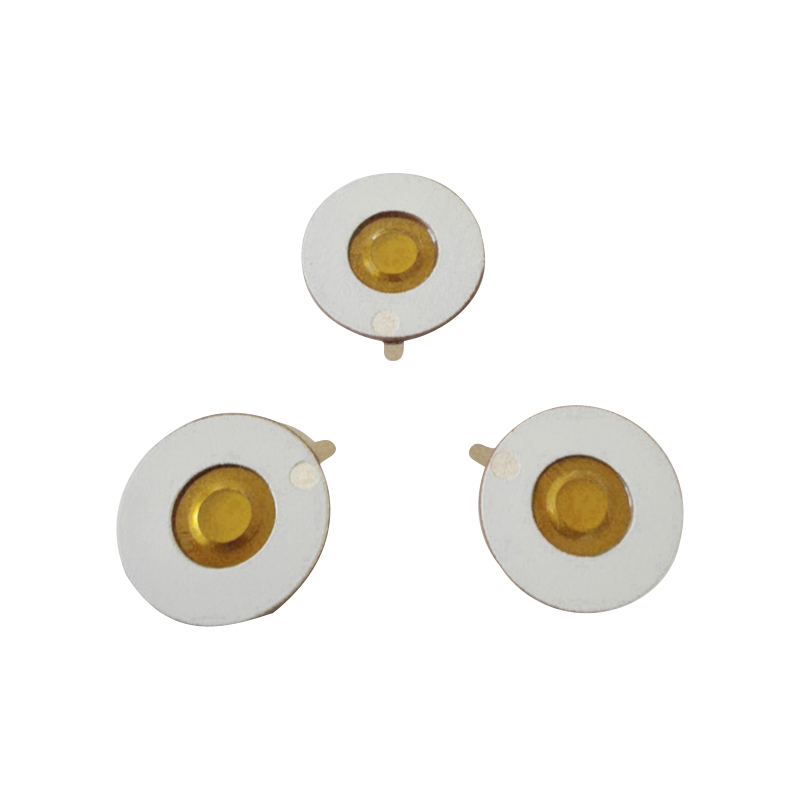
Piezo atomization technology uses a piezoelectric element to generate vibrations. These vibrations are used to break up liquid into fine droplets. The core of this technology is the piezo atomization chip, which is a small device containing a piezoelectric material that changes shape when an electric field is applied. This deformation creates high-frequency vibrations, which are then transferred to the liquid, causing it to atomize.
Working Principle of Piezo Atomization:
- A piezoelectric chip generates oscillations when an electric current is applied.
- These oscillations are transferred to a liquid, causing it to break up into tiny droplets.
- The frequency of oscillation and the material properties of the piezoelectric chip control the droplet size.
Advantages:
- Precision: Piezo atomization provides highly controlled droplet sizes, making it ideal for applications that require uniformity, such as in fuel injectors or medical inhalers.
- Energy Efficiency: Piezoelectric systems consume less energy compared to other methods, as they don’t require high-pressure pumps or complex mechanical systems.
- Compact Design: Piezo atomization chips are small and can be integrated into compact devices, making them suitable for portable and miniaturized applications.
- Low Maintenance: Since there are fewer moving parts in piezo systems, maintenance is generally minimal.
Applications:
- Fuel injectors in modern engines
- Aerosol dispensers
- Medical devices such as inhalers
- Printing technology
Traditional Atomization Technologies
Traditional atomization methods include mechanical atomization, ultrasonic atomization, and thermal atomization. These methods have been in use for decades, with their own set of advantages and limitations.
Mechanical Atomization
Mechanical atomization relies on mechanical energy to break up the liquid. It typically involves high-speed rotating disks or nozzles that force the liquid through small openings, creating fine droplets.
Working Principle:
- The liquid is forced through a nozzle or disk at high speed.
- The high-speed flow of liquid breaks into droplets upon exiting the nozzle.
Advantages:
- Simple and widely understood technology.
- Suitable for large-scale industrial applications like fuel injection systems.
Drawbacks:
- Energy consumption can be higher due to the need for high-pressure pumps.
- Larger in size and often not as precise in droplet control.
Ultrasonic Atomization
Ultrasonic atomization uses ultrasonic waves to generate high-frequency sound vibrations. These vibrations cause the liquid to break into droplets. Ultrasonic atomizers are often used in applications requiring fine mist production.
Working Principle:
- High-frequency sound waves (ultrasonic waves) are transmitted through a liquid.
- The pressure variations caused by these waves break the liquid into fine droplets.
Advantages:
- Produces a very fine mist, making it ideal for medical and industrial applications requiring precise control over droplet size.
- Non-mechanical, reducing wear and tear.
Drawbacks:
- Can be energy-intensive at large scales.
- Can require more maintenance compared to piezo-based systems.
Thermal Atomization
Thermal atomization involves heating the liquid to a point where it evaporates into fine particles. This is commonly used in applications like fuel injectors or combustion systems, where the goal is to atomize the liquid fuel before ignition.
Working Principle:
- Heat is applied to the liquid, causing it to evaporate and form a vapor or fine mist.
- The vaporized liquid is then mixed with air for combustion or other processes.
Advantages:
- Simple and effective in applications where heating is required anyway (e.g., in combustion engines).
- Often used in automotive and aerospace industries.
Drawbacks:
- High energy consumption due to heating.
- Less precise in controlling droplet size.
Key Differences Between Piezo and Traditional Atomization
Below is a comparison table outlining the key differences between piezo and traditional atomization technologies.
| Aspect | Piezo Atomization | Traditional Atomization |
|---|---|---|
| Working Principle | Piezoelectric vibration causes liquid atomization. | Mechanical, ultrasonic, or thermal energy used to break liquid into droplets. |
| Droplet Size Control | Highly precise, controlled by frequency and vibration. | Less precise; larger droplets in mechanical, ultrasonic, and thermal methods. |
| Energy Consumption | Low energy consumption. | Generally higher energy consumption. |
| Design Complexity | Compact and minimal moving parts. | Can be larger, with more complex systems. |
| Applications | Medical devices, aerosol dispensers, fuel injectors, printing. | Large-scale industrial applications, fuel injection, humidification. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance. | Higher maintenance, especially with mechanical and ultrasonic methods. |
| Precision | High precision, ideal for fine mist and uniformity. | Less precise, particularly in mechanical methods. |
Advantages and Drawbacks Comparison
Advantages of Piezo Atomization:
- High Precision: Piezo atomization chips allow for fine control over droplet size, which is essential in applications like medical inhalers or fuel injectors.
- Energy Efficiency: Piezoelectric systems are energy-efficient, making them more suitable for portable or battery-powered applications.
- Durability: The lack of moving parts makes piezo atomization systems highly durable and low-maintenance.
Drawbacks of Piezo Atomization:
- Limited Scale: Piezo systems may not be suitable for very large-scale industrial applications where high volumes of liquid need to be atomized quickly.
- Cost: Piezo atomization chips may have a higher initial cost compared to traditional methods.
Advantages of Traditional Atomization:
- High Flow Rate: Traditional atomization methods, particularly mechanical and thermal, can handle large volumes of liquid.
- Simplicity: Mechanical systems are straightforward and widely used in industrial settings.
Drawbacks of Traditional Atomization:
- Energy Intensive: Traditional methods tend to consume more energy, especially when large volumes need to be processed.
- Less Control Over Droplet Size: Traditional systems may not offer the same level of precision, leading to variability in droplet sizes.
Conclusion
Both piezo and traditional atomization technologies have their own strengths and limitations. Piezo atomization, driven by piezo atomization chips, excels in applications requiring precision, energy efficiency, and compactness. It is especially useful in medical devices, fuel systems, and aerosol dispensers. Traditional atomization methods, on the other hand, are better suited for large-scale, high-flow applications where precise control over droplet size is less critical.
The choice between piezo and traditional atomization will ultimately depend on the specific requirements of the application, including energy efficiency, size constraints, and the level of precision needed.
FAQ
1. What is a piezo atomization chip?
A piezo atomization chip is a small device that uses piezoelectric material to generate vibrations, which are transferred to a liquid to atomize it into fine droplets.
2. How does piezo atomization compare to ultrasonic atomization?
Piezo atomization is more energy-efficient and offers higher precision, while ultrasonic atomization tends to consume more energy and may be less precise in droplet size control.
3. What are the main applications of piezo atomization?
Piezo atomization is widely used in medical devices like inhalers, fuel injectors, aerosol dispensers, and printing technologies.
4. Which atomization technology is better for large-scale industrial applications?
Traditional atomization methods like mechanical or thermal atomization are better suited for large-scale industrial applications due to their ability to handle high volumes of liquid.
5. Is piezo atomization cost-effective for commercial use?
While piezo atomization systems may have a higher initial cost, their energy efficiency and low maintenance make them cost-effective in the long run, particularly for precision applications.



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体